Friday, August 22, 2008
Free Electronic Parts -- Resistors
The resistor's function is to reduce the flow of electric current.
This symbol is used to indicate a resistor in a circuit diagram, known as a schematic.
Resistance value is designated in units called the "Ohm." A 1000 Ohm resistor is typically shown as 1K-Ohm ( kilo Ohm ), and 1000 K-Ohms is written as 1M-Ohm ( megohm ).
There are two classes of resistors; fixed resistors and the variable resistors. They are also classified according to the material from which they are made. The typical resistor is made of either carbon film or metal film. There are other types as well, but these are the most common.
The resistance value of the resistor is not the only thing to consider when selecting a resistor for use in a circuit. The "tolerance" and the electric power ratings of the resistor are also important.
The tolerance of a resistor denotes how close it is to the actual rated resistence value. For example, a ±5% tolerance would indicate a resistor that is within ±5% of the specified resistance value.
The power rating indicates how much power the resistor can safely tolerate. Just like you wouldn't use a 6 volt flashlight lamp to replace a burned out light in your house, you wouldn't use a 1/8 watt resistor when you should be using a 1/2 watt resistor.
The maximum rated power of the resistor is specified in Watts.
Power is calculated using the square of the current ( I2 ) x the resistance value ( R ) of the resistor. If the maximum rating of the resistor is exceeded, it will become extremely hot, and even burn.
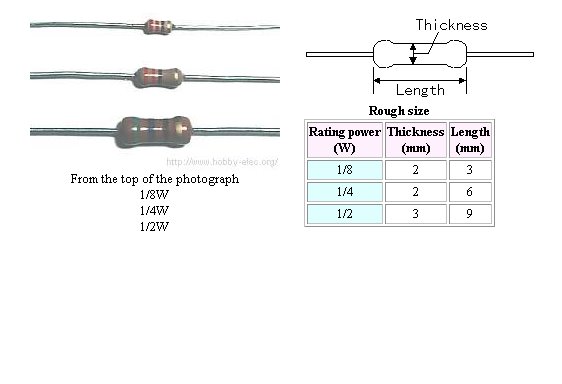
Resistors in electronic circuits are typicaly rated 1/8W, 1/4W, and 1/2W. 1/8W is almost always used in signal circuit applications.
When powering a light emitting diode, a comparatively large current flows through the resistor, so you need to consider the power rating of the resistor you choose.
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)